Chapter 5: Further Topics in Functions, Precalculus 3e Stitz/Zeager
5.1 Function Composition
Composition of Function
The composition of a function \(f\) with a function \(g\) is:
\[(f \circ g)(x) = f(g(x))\]
The domain of \((f \circ g)\) is the set of all \(x\) in the domain of \(g\) such that \(g(x)\) is in the domain of \(f\).
- \((f \circ g)(x) = f(g(x)) = f(x - 1)\)
- \((g \circ f)(x) = g(f(x)) = g(x^3 +2x +1)\)
- \((f \circ f)(x) = f(f(x)) = f(x^3 +2x +1)\)
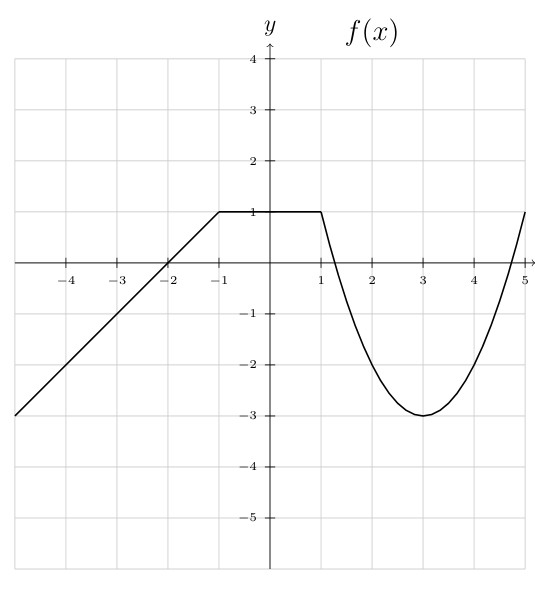
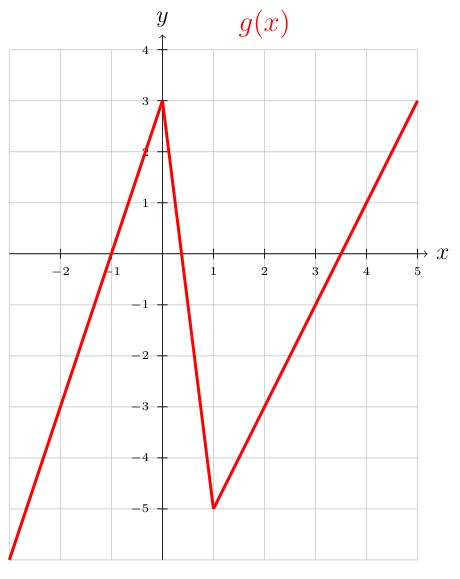
- \(f(g(1))\)
- \(g(f(2))\)
- \(f(g(0))\)
- \(g(f(0))\)
- \(f(g(-2))\)
- \(g(f(-2))\)
5.2 Inverse Functions
One to one functions
A function is said to be one to one (1-1) if no two ordered pairs have the same second component but different first component.
A function has one \(y\) value for each \(x\) value but those \(y\) values can repeat. In a 1-1 function the \(y\) values never repeat.
Graphically:
An equation must pass the Vertical Line Test to be a function.
A function must pass the Horizontal Line Test to be 1-1.
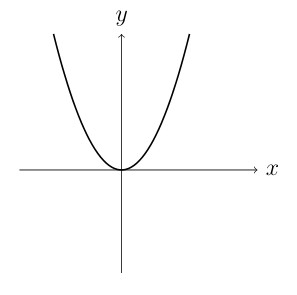
NOT 1-1 (fails horizontal line test)
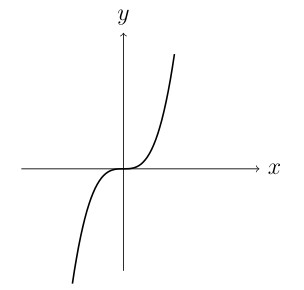
IS 1-1 (passes horizontal line test)
Inverses
The identity function is \(f(x) = x\) or \(y = x\). You get out what you put in. Given a function \(f\) that is 1-1 then \(f\) has an inverse \(f^{-1}\) and:
\[f(f^{-1}(x)) = x \qquad \text{and} \qquad f^{-1}(f(x)) = x\]
If \(f\) is not 1-1 then \(f^{-1}\) DOES NOT EXIST.
Graphically
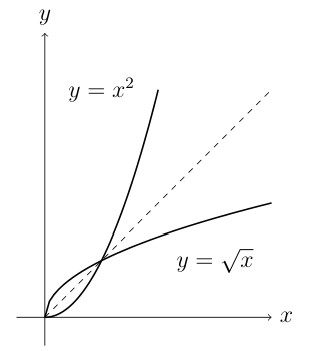
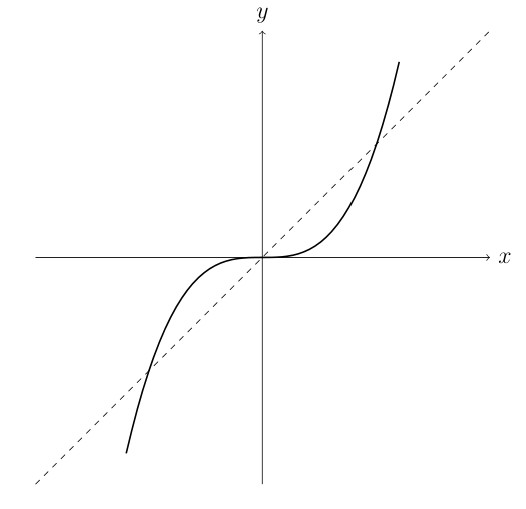
Finding inverses from tables and graphs
| \(x\) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| \(f(x)\) | 8 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 9 | 3 | 0 |
\(f(2) =\)
if \(f(x)=4\) then \(x =\)
\(f^{-1}(5) =\)
if \(f^{-1}(x) =1\) then \(x =\)
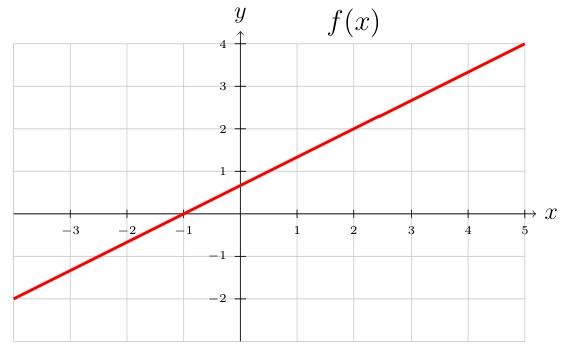
\(f(2) =\)
if \(f(x)=4\) then \(x =\)
\(f^{-1}(-2) =\)
\(f^{-1}(0) =\)
if \(f^{-1}(x) =5\) then \(x =\)
Finding Inverses Algebraically
Step 1: Solve for \(x\).
Step 2: Check the domain.
Step 3: Switch \(x\) and \(y\).
Step 4: Write \(f^{-1}(x) =\)
Step 5: Check that \(f(f^{-1}(x)) = x\).
Step 1: Solve for \(x\). (two answers here)
Step 2: Check the domain.
Step 3: Switch \(x\) and \(y\).
Step 4: Write \(f^{-1}(x) =\)
Step 5: Check that \(f(f^{-1}(x)) = x\).